
The base current is generated by a second 0V-to-12V DAC and a 27k resistor. The Arduino measures the voltage between the collector and emitter and the voltage across the load resistor and draws a graph. A DAC controlled by the Arduino sweeps that test voltage from 0V to 12V (or until the current through the load resistor reaches 50mA). The emitter of the NPN is connected to 0V and the collector is connected to a 100ohm "load resistor" and then to a voltage that slowly increases. We'll draw one line for each different base current (Ib) - e.g. We're going to draw a graph of the voltage between the collector and emitter (x-axis is Vce) versus the current flowing into the collector (y-axis is Ic). In the image above, I've combined the curves of several diodes. With diodes, you can see the forward voltage and with Zeners, the reverse breakdown voltage.

You can select the minimum and maximum gate voltage: more curves will be drawn in that region.įor a PNP or NPN transistor, the Setup screen allows you to select the minimum and maximum base current In the main menu, touch the Setup button and the Setup screen will be shown.
TRANSISTOR TESTER DIAGRAM PLUS
The most interesting part of a MOSFET or JFET curve is around the turn-on or cut-off voltage plus or minus a few hundred mV. The cut-off threshold of the FET is shown at the top of the screen. As the gate voltage is changed to be further from the drain voltage, the JFET turns off. With depletion JFETs, current flows when the gate voltage is equal to the source voltage. A line is drawn for each different gate voltage - 0V, 1V, 2V, etc. The turn-on threshold of the FET is shown at the top of the screen.įor a JFET it plots Vds (the voltage between the drain and source) versus the current flowing into the drain. The gain of the transistor is shown at the top of the screen.įor a MOSFET it plots Vds (the voltage between the drain and source) versus the current flowing into the drain. A line is drawn for each different base current - e.g. Close the ZIF socket.Īfter a second or so, the tester will realise that it has a component and will start to draw the curves.įor a PNP or NPN transistor it plots Vce (the voltage between the collector and emitter) versus the current flowing into the collector. NPNs, n-channel MOSFETS and p-channel JFETS go in the right side of the socket.
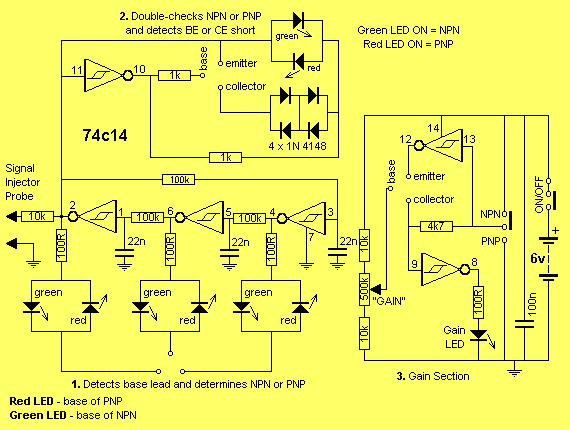
PNPs, p-channel MOSFETS and n-channel JFETS go in the left side of the socket. The menu screen shows you which pins to use. Put the Device Under Test (DUT) into the ZIF socket. You can test diodes in the "PNP NPN" mode. Select the kind of device by touching one of "PNP NPN", "MOSFET" or "JFET". When you switch on the curve tracer, the main menu screen is displayed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
